May 21, 2024
Type 1 Diabetes vs Type 2 Diabetes
What is the Difference Between Type 1 Diabetes and Type 2 Diabetes? If you’ve recently been diagnosed with diabetes, you’re probably searching for clear answers about the differences between Type 1 diabetes and Type 2 diabetes. We know it can…
Share This Story
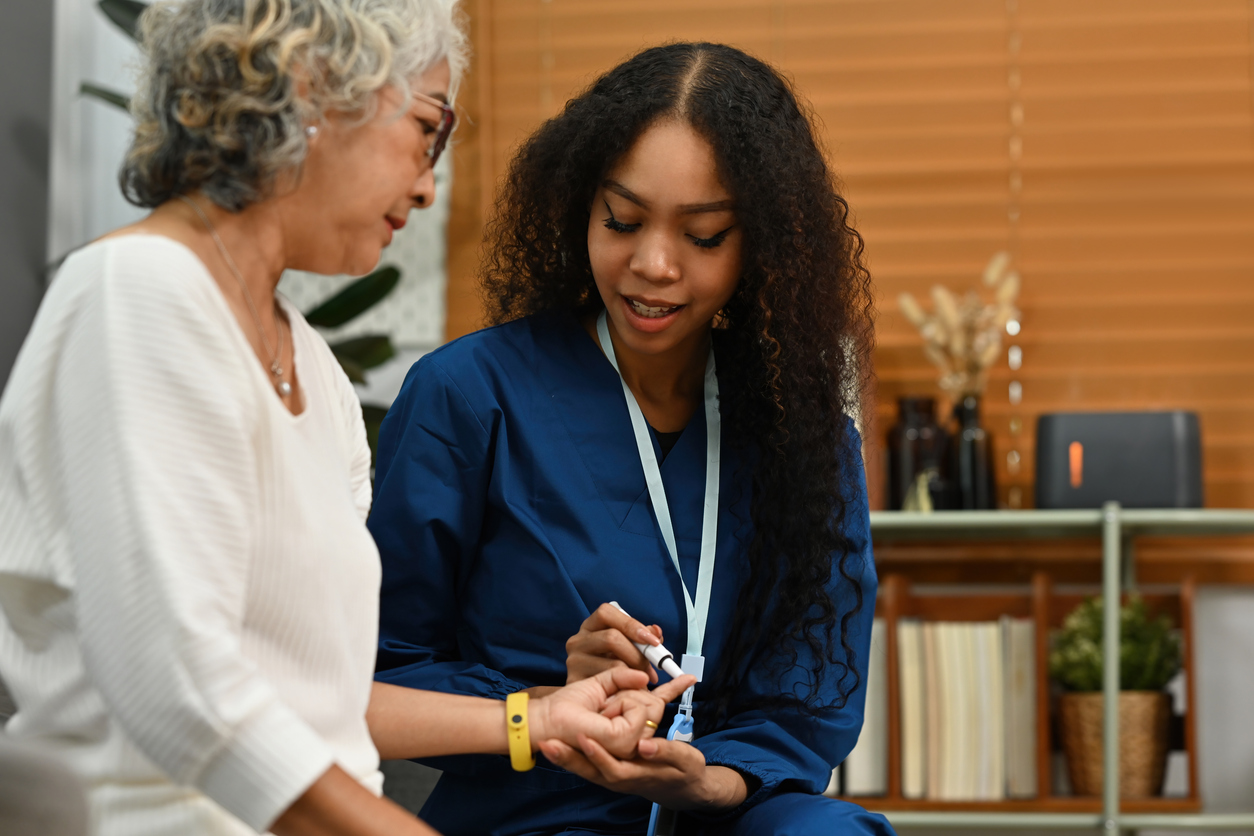

What is the Difference Between Type 1 Diabetes and Type 2 Diabetes?
If you’ve recently been diagnosed with diabetes, you’re probably searching for clear answers about the differences between Type 1 diabetes and Type 2 diabetes. We know it can feel overwhelming, so we’re here to help distinguish between these two forms of the condition. Both involve challenges with insulin and blood sugar, yet they differ significantly in symptom onset, warning signs, and management.
![]()
Written by: US MED Staff
Clinically Reviewed by: Shirley DeLeon, RD, CDCES
Understanding these differences is crucial for anyone living with diabetes. Whether you’re new to these terms or need a refresher, this guide from US MED will provide you with an in-depth comparison of Type 1 diabetes and Type 2 diabetes to help you navigate your journey with clarity.
What is type 1 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is no longer the most common form of diabetes, but it remains quite prevalent. Over a million people are believed to have this type of diabetes in the U.S. alone.
Regardless of what type of diabetes they have, people with diabetes have excessively high glucose levels in their blood. The reason why this is the case differs between these conditions. Type 1 diabetes is considered an autoimmune condition – that is to say, your body attacks healthy cells. The cells targeted with this condition are located in the pancreas and are responsible for making insulin; as a result, you eventually become unable to make this substance on your own.
What are the symptoms of type 1 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is most commonly diagnosed in childhood, typically emerging during two key age ranges: between four and seven years old, and between ten and fourteen years old. Although it’s less common, adults can also be diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes. Parents and guardians should be vigilant for symptoms that may signal the onset of this condition, which include:
 Blurry vision
Blurry vision- Slow-healing wounds
- Itching in the genital region
- Unexpected weight loss
- Unusual tiredness
- Extreme thirst
- Excessive urination, especially at night
While these symptoms can also appear in Type 2 diabetes, the age at which they present is a crucial differentiator. Understanding these signs is important, but it’s equally vital to recognize the broader diabetes risk factors that can affect individuals at any age.
What diabetes risk factors are considered with Type 1?
T1D manifests through specific diabetes risk factors that can indicate a higher likelihood of developing this condition. Here’s a deeper look into the warning signs that may signal the presence of type 1 diabetes:
- Family History: Genetics play a significant role in type 1 diabetes. If a close family member has been diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, the risk of developing it increases due to shared genetic markers that can predispose individuals to this autoimmune response.
- Environmental Factors: Certain environmental triggers, such as exposure to viral illnesses, are believed to activate the autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Viruses like enteroviruses, mumps, and rubella are among those implicated in possibly triggering this autoimmune process.
- Autoantibodies: These are immune system cells that mistakenly attack one’s own body, the immune system identifies healthy pancreatic cells as invaders. Detecting these autoantibodies in the blood can often predict the onset of type 1 diabetes before symptoms even appear, providing a crucial window for early intervention.
- Geographic Location: Epidemiological studies have noted varying incidence rates of type 1 diabetes across different regions, with notably high rates in countries like Finland and Sweden. This variation suggests that geographic and perhaps related environmental factors might influence the prevalence of this condition.
Understanding these risk factors is vital for early diagnosis and management of type 1 diabetes. Awareness and regular screening, especially if risk factors are present, can lead to timely treatment and better health outcomes.
How is type 1 diabetes diagnosed?
If you or your doctor suspect you have type 1 diabetes, you’ll need to complete a blood screening. The most common blood test used in diabetes diagnosis is known as an A1C screening, which measures your blood sugar levels over two or three months.
How to treat type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is a lifelong condition with no known cure. However, you can manage this disease and live a fulfilling life by:
- Taking insulin as needed. Since you can’t make your own insulin with type 1 diabetes, you need a steady supply of insulin to survive. You can administer this medication with injections or an insulin pump.
- Following a diabetes diet. Though there isn’t a single diabetes diet you’ll need to stick to, try to limit your intake of processed carbs and eat nutritious foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources.
 Getting exercise regularly. That doesn’t have to mean doing an intense workout every day – just try to get half an hour of moderate physical activity most days of the week.
Getting exercise regularly. That doesn’t have to mean doing an intense workout every day – just try to get half an hour of moderate physical activity most days of the week.- Tracking your blood sugar. Regular blood sugar measurements can help you understand how well your treatment regimen is working. You may need to take anywhere between four to 10 measurements daily.
What is type 2 diabetes?
On the surface, type 2 diabetes is very similar to type 1 diabetes. However, the two conditions have some crucial differences.
If you have type 2 diabetes, your pancreas may still be able to produce some insulin. The problem lies in “insulin resistance” – essentially, your body has trouble using insulin as effectively as it should. That means your pancreas must work overtime to create extra insulin and may eventually “burn out” as a result.
What are the symptoms of type 2 diabetes?
Most symptoms of type 2 diabetes are also seen in type 1 diabetes. Despite this, the way they can appear is different. Unlike type 1 diabetes symptoms, symptoms of type 2 diabetes often develop slowly over time. As a result, it can be much harder to notice these symptoms early on. Refer back to Type 1 diabetes symptoms up above.
What are the warning signs for type 2 diabetes?
Because spotting type 2 diabetes symptoms can be difficult, it’s imperative to understand the risk factors for type 2 diabetes. These include:
- Having prediabetes (a condition where blood sugar levels are somewhat elevated)
 Having polycystic ovary syndrome
Having polycystic ovary syndrome- Being overweight/obese or storing fat in the belly
- A family history of type 2 diabetes
- Not getting much exercise
- Being Alaska Native, American Indian, Hispanic, or Black
- Being older than 45
- Having given birth to a baby weighing 9+ pounds
- A previous diagnosis of gestational diabetes
How is type 2 diabetes diagnosed?
The process of diagnosing type 2 diabetes is nearly identical to the process of testing for type 1 diabetes. If you think you might have type 2 diabetes, you’ll need to confirm it with an A1C test.
How to treat type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes treatment is also similar to type 1 diabetes treatment. Diet, exercise, and blood sugar measurements can help you manage either one of these illnesses.
The most significant difference between treating the two conditions is that people with type 2 diabetes may not need insulin. If you have type 2 diabetes, talk to your healthcare team about what you need to manage this disease successfully.
How are type 1 and type 2 diabetes the same?
Though they have some major differences, type 1 and type 2 diabetes are both tied to problems with insulin production. Cells in the body need insulin to access the sugar in the bloodstream, which they use as a source of fuel. Diabetes creates problems in this regard since the body cannot use or produce insulin as it should. On top of this, type 1 and 2 diabetes share common symptoms, diagnosis methods, and treatment strategies.
How are type 1 and type 2 diabetes different?
On the other hand, you shouldn’t discount the factors separating type 1 and 2 diabetes. Since their root causes differ, you may need to make some changes to your treatment regimen as a result (such as taking insulin with type 1 diabetes). The onset of symptoms can vary between these types of diabetes, and they have separate sets of risk factors. Additionally, type 1 diabetes is more common in children and type 2 diabetes is often seen in older adults.
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes prevention & diets
 Another difference between type 1 and 2 diabetes is that during the prediabetes window you may be able to prevent type 2 with diet and exercise, while type 1 cannot. Either way, you should consider eating a healthy diet t if you are at risk for either disease. Though a healthy diet cannot slow or reverse the progress of type 1 diabetes, it can make it easier to manage this condition.
Another difference between type 1 and 2 diabetes is that during the prediabetes window you may be able to prevent type 2 with diet and exercise, while type 1 cannot. Either way, you should consider eating a healthy diet t if you are at risk for either disease. Though a healthy diet cannot slow or reverse the progress of type 1 diabetes, it can make it easier to manage this condition.
Here are some of the food groups to focus on while following a diabetes diet:
- Fresh produce. Many vegetables and fruits are high in fiber, vitamins, and nutrients, all of which can help with diabetes management.
- Protein sources. Along with lean meats and fish, try to get some plant-based proteins like beans in your diet.
- Whole grains. Though they’re still a source of carbohydrates, the fiber found in whole grain products makes them much more nutritious than processed carbs.
- Healthy beverages. Water (including sugar-free flavored sparkling water), black coffee, and unsweetened tea are all great choices.
Meanwhile, aim to avoid oils, fats (including fatty meats), and sweets. While you’ll need to work with your healthcare team to develop the exact healthy diet you should follow, these tips can help you get a head start!
When should I contact a doctor?
Notify your doctor if you notice symptoms of diabetes or if your previously-diagnosed type 1 or 2 diabetes seems to worsen. On top of this, monitoring diabetes closely when you’re sick is crucial, as illnesses can alter your symptoms. Contact your doctor if you notice:
- Difficulties moving your limbs
- Severe pain
- Coordination/balance issues
- Vomiting and nausea that lasts over four hours
- High blood sugar for more than a day
- Fever of at least 100°F
- Memory loss or confusion
How to manage diabetes
When you follow the tips included in this article, you should be able to manage type 1 or type 2 diabetes successfully. However, you’ll also need access to certain supplies to take care of this condition. Some diabetes essentials include:
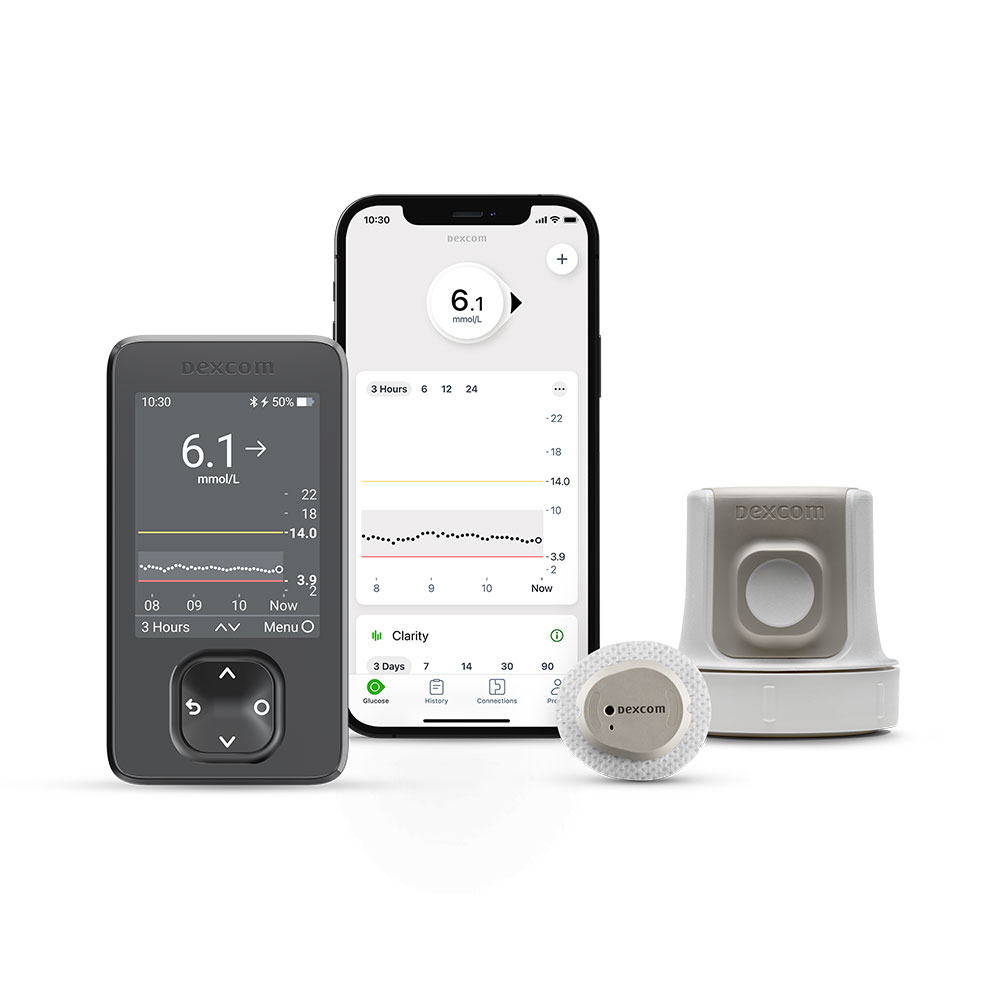
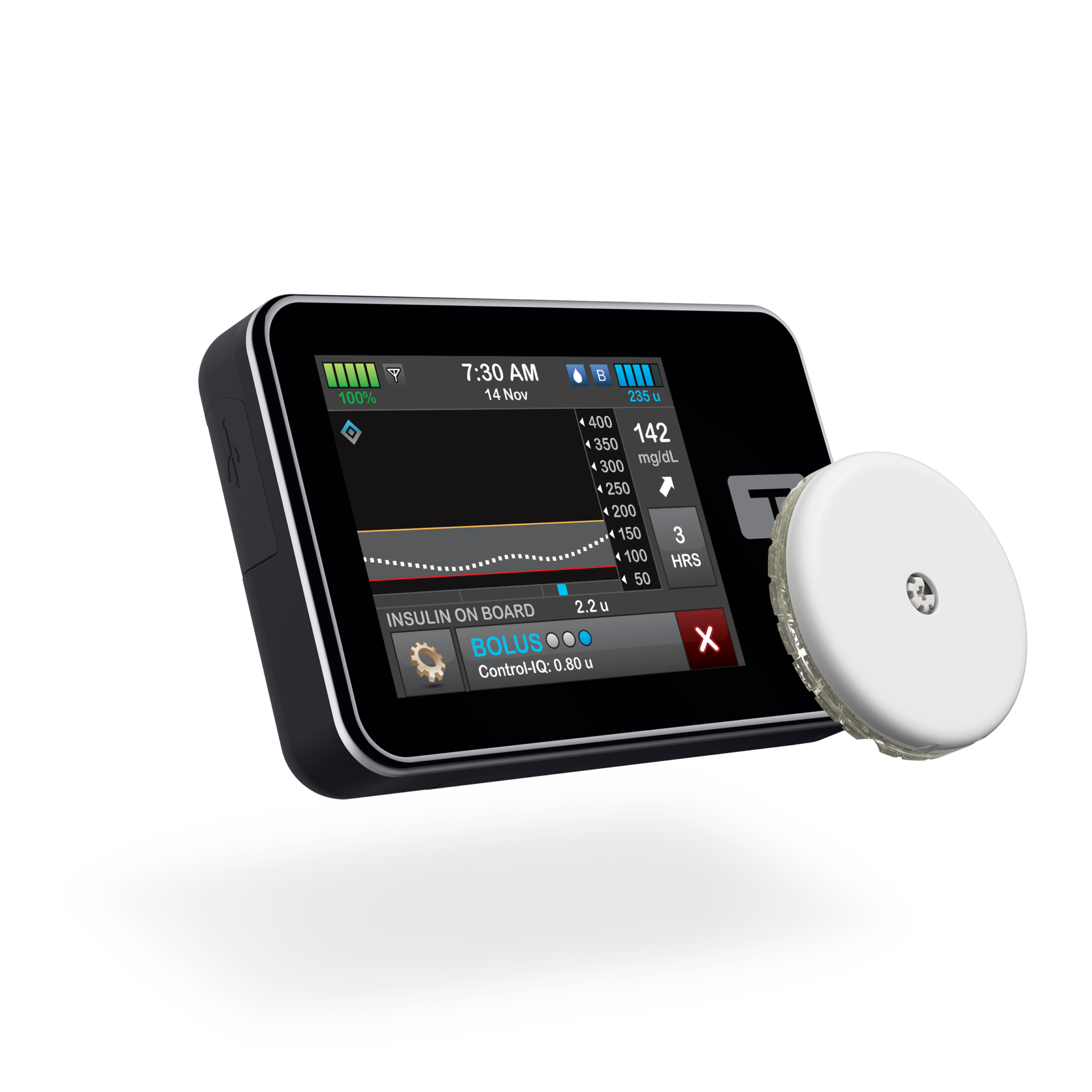
CGM
A continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) system can make life with type 1 or type 2 diabetes considerably easier. With this system, you’ll be able to check your glucose levels by wearing a sensor. These devices can’t eliminate finger prick tests – if your symptoms don’t match your readings, you’ll still need to double-check with the older testing method. Still, a good CGM can significantly reduce your reliance on these painful tests.
Insulin pumps
Wearable insulin pumps are another way to use technology to reduce the inconveniences tied to diabetes. These products can deliver insulin doses throughout the day. Using them along with a compatible CGM can create a “closed-loop system” capable of providing insulin whenever you need it.
Testing strips
While finger-prick tests are generally a reliable way to test your blood sugar, they can’t operate in isolation. You’ll also need to have access to compatible testing strips – that is, the strips you place a blood sample on while measuring your glucose levels.
Why choose US MED for your diabetes supplies?
As countless people living with type 1 and type 2 diabetes already know, US MED is America’s most trusted provider of diabetes supplies. We offer complimentary priority shipping, direct insurance billing, and a 100-percent satisfaction guarantee.
Taking all that into account, it’s no surprise that we’ve earned an A+ rating from the Better Business Bureau and have been officially recognized by the American Diabetes Association. To experience the US MED difference for yourself, start exploring our online shop today!

 Blurry vision
Blurry vision Getting exercise regularly. That doesn’t have to mean doing an intense workout every day – just try to get half an hour of moderate physical activity most days of the week.
Getting exercise regularly. That doesn’t have to mean doing an intense workout every day – just try to get half an hour of moderate physical activity most days of the week. Having polycystic ovary syndrome
Having polycystic ovary syndrome